Catastrophic conditions created by a climate-induced drought, environmental degradation, a distant war and other factors are now threatening the lives of over 20 million children in Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia, according to UNICEF — more than double the number of children reported just five months ago.
Levels of malnutrition are soaring among children, with 1.9 million children in drought-affected areas projected to need treatment for severe wasting, a life-threatening form of malnutrition, in the coming months.
UNICEF is seeking donor support to accelerate humanitarian action in the region, protect the most vulnerable and save children’s lives.
With severe drought expected to continue, more support is needed to prevent child deaths
“While collective and accelerated efforts have mitigated some of the worst impact of what had been feared, children in the Horn of Africa are still facing the most severe drought in more than two generations,” UNICEF Deputy Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa Lieke van de Wiel said.
“Humanitarian assistance must be continued to save lives and build the resilience of the staggering number of children and families who are being pushed to the edge – dying from hunger and disease and being displaced in search of food, water and pasture for their livestock.”
Over 20m children across #Ethiopia, #Kenya and #Somalia are now facing the threat of severe hunger. We need a global effort to mobilize resources before irreversible damage occurs to #children in the #HornOfAfrica.
We need to ACT NOW #ForEveryChild
—https://t.co/oqPiiCr2v9 pic.twitter.com/VToiRLnDo4— UNICEF Africa (@UNICEFAfrica) December 23, 2022
20.2 million children are now facing threat of severe hunger, thirst and disease in Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia — up from 10 million last July
The drought currently gripping countries all across the Horn of Africa shows no sign of letting up following five straight failed rainy seasons. It’s not the region’s first drought, but by all accounts it is its worst in 40 years — one more natural disaster fueled and compounded by climate change.
Water scarcity has displaced an estimated 2 million people as food and fuel prices have soared amid global inflation and grain shortages linked to the war in Ukraine. Outbreaks of cholera, diarrhea and measles are all on the rise.
By late December 2022, the estimated number of children facing the threat of severe hunger, thirst and disease had jumped to around 20.2 million, compared to 10 million in July.
‘Irreversible’ consequences for children as households turn to dangerous coping strategies
To survive, families are adopting coping strategies that have dangerous and often irreversible consequences for children, UNICEF warns. These include reducing food intake, withdrawing children from school (to save money on school fees or to send children to work), selling off assets (livestock, household items or land), pushing girls into early marriage, and migrating to urban centers in search of assistance.
Close to 3 million children are out of school with millions more at risk of dropping out.
“We’ve actually seen the consequences directly,” Deputy Regional Director for UNICEF in Eastern and Southern Africa Rania Dagash told the BBC last month. “[C]hildren face a wide range of dangers, from child labor to a doubling of child marriage numbers and female genital mutilation. We’ve seen a lot more intensity than we have ever seen before.”
Fundamentally, Dagash added, “this is a water crisis, a nutrition crisis, a health one — and when combined with chronic conflict and rising food prices and disease, it creates a nightmare for children, especially in Somalia.”
Widespread food insecurity is attributed to the drought, which destroyed crops, killed cattle and destroyed livelihoods. But the war in Ukraine has further aggravated the situation. Countries in the Horn of Africa region depend on grain imports from both Russia and Ukraine, leaving them vulnerable to the war’s adverse effects on food production and supply chains. “Food prices are exponentially high for people who are already in dire straits,” Dagash said.
What UNICEF is doing to help children and families caught in Horn of Africa drought crisis
Current humanitarian aid funding levels for the Horn of Africa drought crisis response are far below what is needed to cover immediate and long-term aid goals as set out in UNICEF’s action plan for 2023.
That plan encompasses a broad range of interventions, from staffing and supplying mobile health and nutrition teams delivering emergency care to at-risk children to providing health facilities with lifesaving Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) to treat children suffering from severe acute malnutrition (SAM). In the first 10 months of 2022, UNICEF and partners reached nearly 684,000 children across Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia with lifesaving treatment for SAM.
The Government of Kenya is leading the drought response at the national and county level, with support from UNICEF and partners. This includes emergency supplies to provide families with access to safe drinking water. Above, a boy drinks from a safe water point in Daley Village, Garissa County. © UNICEF/UN0641786/Orina
As the lead UN agency for water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) needs, UNICEF is providing access to clean water and reliable sanitation, while promoting basic hygiene practices in rural and urban areas to strengthen disease prevention. In 2022, UNICEF reached over 2.7 million people in the Horn of Africa region with safe water for drinking, cooking and washing. UNICEF is also working with partners to develop climate-sensitive water infrastructure in drought-prone areas.
In education, UNICEF is helping displaced children get back to learning, providing protective safe spaces where children can also access critical health, nutrition and water services, along with mental health and psychosocial support. In 2022, UNICEF reached nearly 2 million children and women in the Horn of Africa region with essential lifesaving health care services — and vaccinated close to 2 million children against measles.
More support is needed to accelerate emergency response efforts across all program areas. UNICEF’s 2023 plan asserts that both response pillars — the emergency relief and the resilience building and system strengthening work — “require equal attention and support” as children and families continue to be worn down year after year, with no time for recovery.
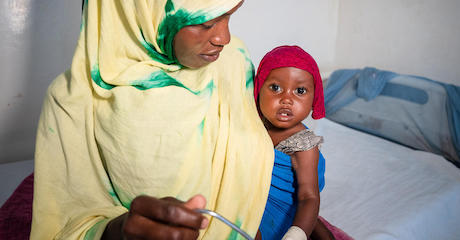
In Puntland, Somalia, 1-year-old Aisha and her mother are greeted by Dr. Isse Hassan at Garowe General Hospital Stabilization Center where Aisha is undergoing treatment for severe acute malnutrition. She arrived in critical condition and was given oxygen, glucose and amoxicillin. Ater three days, she was faring much better. UNICEF supports the stabilization center with funding from USAID. © UNICEF/UN0750377/Ekpu VII Photo
Making smart investments in climate resilience, and building social safety nets
While continuing to ramp up assistance in the region, UNICEF continues to make smart investments in the longer-term resilience of communities and their children through its WASH programming — including drilling for reliable sources of groundwater using sateillte maps and probes to identify deep aquifers.
UNICEF is also focused on strengthening government social protection systems, which includes expanding humanitarian cash transfer programs — critical support that helps families who have lost their livelihoods meet basic needs.
Protecting children and women from violence
Together with partners, UNICEF is also responding to increased risks of gender-based violence (GBV) fueled by economic hardships and social strife that comes with widespread food insecurity and displacement.
A growing number of women and girls are forced to travel longer distances to secure water, food and firewood for their families, leaving them vulnerable to sexual violence. Female-headed households, adolescent girls, older women and those with disabilities are at heightened risk.
UNICEF supports GBV prevention and case management and works in communities to end FGM and child marriage.
Help UNICEF reach more children and families in need in the Horn of Africa. More funding is needed to save children’s lives, preserve their dignity and protect their futures. Donate today.
Top photo: Aisha, a young patient at UNICEF-supported Garowe General Hospital Stabilization Center, part of the hospital complex that treats children under 5 who are suffering from severe acute malnutrition (SAM) in Puntland, Somalia. Many come from remote rural areas as far away as 150 miles, or from nearby displacement camps. UNICEF is scaling up all nutrition interventions as the drought crisis continues to grip the country. © UNICEF/UN0750379/Ekpu VII Photo